Domain name

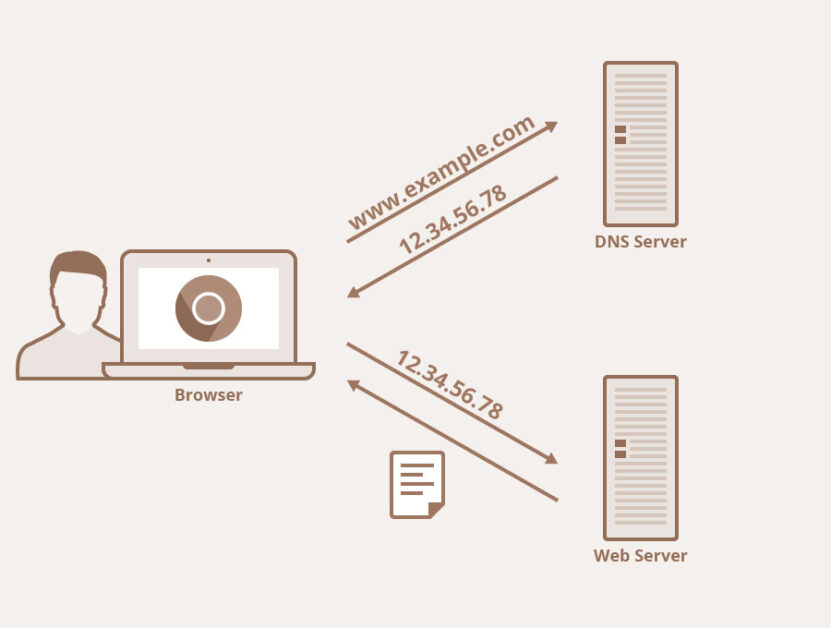
A domain name is a unique address that identifies a website on the internet. It serves as a user-friendly way to access websites and is typically made up of two main parts: the domain name itself and the domain extension.
The domain name is the part that you choose and register, such as “example” in the domain name “example.com”. It can be a combination of letters, numbers, and hyphens. The domain extension, also known as a top-level domain (TLD), comes after the domain name and indicates the purpose or geographical location of the website. Some popular domain extensions include:
- .com: This is the most popular and widely recognized domain extension, originally intended for commercial websites but now used by various types of organizations.
- .org: Originally meant for non-profit organizations, this domain extension is now used by a variety of groups, including non-profit entities, schools, and communities.
- .net: Initially intended for network-related organizations, this domain extension is now used by a wide range of websites.
- .edu: Restricted to accredited educational institutions such as universities and colleges.
- .gov: Reserved for government entities and agencies.
- .io: Originally representing the British Indian Ocean Territory, it has become popular among tech startups and companies due to its association with “input/output.”
- .co: Originally assigned to Colombia, it is now widely used as an alternative to .com for commercial websites.
- .info: Suitable for informational websites or resources.
- .me: Often used for personal websites or blogs.
- .xyz: A generic and versatile domain extension that gained popularity due to its availability and ease of use.
These are just a few examples, and there are many other domain extensions available. The choice of domain extension depends on the purpose and nature of the website you are creating.
Some popular domain registrars are
- GoDaddy: GoDaddy is one of the largest domain registrars and web hosting companies globally. It offers a wide range of domain name extensions and additional services.
- Namecheap: Namecheap is known for its affordable domain registration and offers various domain extensions. They also provide additional features like Whois privacy protection.
- Bluehost: Bluehost is primarily a web hosting provider, but they also offer domain registration services. They provide a free domain name for the first year with their hosting plans.
- Google Domains: Google Domains is a domain registration service by Google. It offers a straightforward and user-friendly interface, along with additional features like domain management tools and email forwarding.
- Domain.com: Domain.com provides domain registration services and offers a variety of domain extensions. They also provide web hosting, email, and website builder services.
It’s important to note that the popularity of domain registrars can change over time, and there may be other domain registrars that have gained popularity since my knowledge cutoff date. It’s always a good idea to research and compare different registrars to find the one that best suits your specific needs.
Everything you need to know about domain names
Domain registration cost, Renewal period , What happens after domain expires
The cost of domain registration can vary depending on the domain registrar and the specific top-level domain (TLD) you choose. Generally, the cost can range from a few dollars to several hundred dollars per year. Popular TLDs like .com, .net, and .org tend to have higher registration fees compared to less common TLDs.
The renewal period for most domains is typically one year, although some registrars offer longer renewal periods, such as two or more years. It’s important to note that the renewal period can vary depending on the specific TLD and registrar policies.
When a domain registration expires, several things can happen:
- Grace Period: Many registrars provide a grace period after the expiration date, during which you can renew the domain without any additional fees. The length of the grace period varies between registrars, but it’s usually around 30 days. During this period, your website and email associated with the domain may continue to function.
- Redemption Period: After the grace period, the domain enters a redemption period. During this phase, you can still renew the domain, but there is usually an additional fee imposed by the registrar. The redemption period typically lasts for about 30 days, although the duration can vary.
- Auction or Release: If you do not renew the domain during the redemption period, it may be released back into the pool of available domains for registration. In some cases, expired domains may go through an auction process, where interested parties can bid on them. The specific process for releasing expired domains can vary depending on the registrar’s policies.
It’s essential to keep track of your domain’s expiration date and ensure timely renewal to avoid any disruption to your website or email services.
FAQ
To register a domain name, you need to find a domain registrar, which is a company accredited to sell and manage domain names. You can search for available domain names on their website, select the one you want, and follow their registration process. You will need to provide your contact information and pay a registration fee for a specific duration (usually 1 to 10 years).
Yes, you can transfer your domain from one registrar to another. The process typically involves unlocking the domain, obtaining an authorization code (also known as an EPP code), and initiating the transfer with the new registrar. Both the current and new registrars may have specific steps and requirements for the transfer, so it’s important to follow their instructions.
Domain privacy protection, also known as WHOIS privacy, is a service offered by some registrars to keep your personal contact information private in the publicly accessible WHOIS database. By enabling domain privacy protection, the registrar replaces your personal details with their own or a proxy’s information, shielding your email address, phone number, and physical address from potential spammers, telemarketers, or identity thieves.
Yes, you can have multiple domain names pointing to the same website. This is commonly referred to as domain aliasing or domain forwarding. By setting up proper domain forwarding or configuring DNS records, you can direct multiple domains to the same website, allowing users to access your site through different domain names while maintaining a single web presence.
